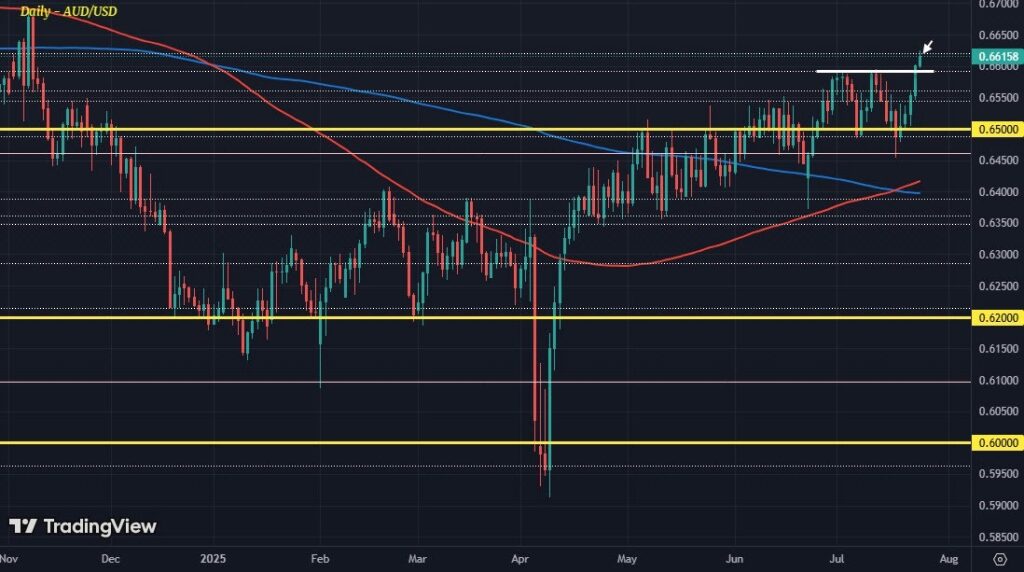
July 24–25, 2025 — The Australian Dollar (AUD) surged to fresh eight‑month highs, crossing above USD 0.6600 as markets embraced a risk-on mood, while the US Dollar (USD) softened under pressure from improving global sentiment and weaker US economic expectations.
📈 Markets Rally, Risk Appetite Returns
Asian equities saw strong gains during Thursday trading after upbeat corporate earnings and incremental progress in US trade negotiations with the EU and Japan. This positive environment lifted investor confidence and supported demand for risk-sensitive currencies like the AUD .
🇦🇺 Australia’s PMI Strengthens
Australia’s S&P Global Composite PMI rose to 53.6 in July, marking the highest level since April 2022 and signaling healthy expansion in the services and manufacturing sectors. This upbeat data reinforced expectations of domestic economic resilience, further boosting the AUD .
🇺🇸 US Dollar Weakens on Trade and Fed Speculation
Improving trade outlook—particularly US-Japan and US-EU talks—helped weaken the USD. The US Dollar Index (DXY) fell toward the mid‑97 level, reflecting diminished haven demand and easing fears around inflation and Fed policy tightening .
🔍 AUD/USD Outlook
technicians view the eight‑month high near 0.6619 as the latest pivotal level. If the pair consolidates above this zone, it could aim toward 0.665–0.6700. On the downside, support now sits around 0.6540–0.6520, aligned with the 9‑day EMA zone .
🏦 Central Bank Policy Signals
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) held its cash rate at 3.85% in early July and signaled economic stability but left expectations for eventual easing intact. Markets currently price in an RBA cut as soon as August, though the timing may be cautious. UBS and other analysts continue to project modest AUD appreciation through year‑end, with forecasts around USD 0.67–0.68 .
🪙 Commodities and Long‑Term Drivers
Australia’s exposure to iron ore, gold, copper, and LNG exports continues to tie AUD movements to global commodity cycles. Institutions forecast that commodity strength and stabilizing Chinese stimulus will remain supportive, even as rate differentials narrow .
